Introduction to on-page SEO:
The practice of enhancing various front-end and back-end components of your website in order to better its position in search results and draw in more visitors is known as on-page SEO, also referred to as on-site SEO. On-page SEO consists of content components, site architectural elements, and HTML elements.
On-page SEO is essential since it tells Google about your website and how you create value for users and customers. It helps with website optimization for both human visitors and search engine robots. Your website must be optimized for Google and other search engines in addition to being designed and published if you want it to rank well and attract new visitors.
The changes you make to your website to optimize it are visible to visitors, unlike off-page and technical SEO factors, which are not always obvious. On-page SEO is known as “on-page”
On-page SEO is all up to you, thus it’s essential that you execute it properly. Let’s now talk about the components of on-page SEO.
On-Page SEO Elements:
- High-Quality Page Content
- Page Titles
- Headers
- Meta Descriptions – ( increase CTR Only)
- Image Alt-text
- Structured Markup
- Page URLs
- Internal Linking
- Mobile Responsiveness
- Site Speed
Importance of On-Page SEO:
In order to better comprehend user intent and the entire user experience after a user lands on a page, Google adjusts its algorithm on a regular basis. For this reason, it’s crucial to keep up with best practices and master SEO.
Additionally, user experience is a Google priority, therefore it’s important to incorporate on-page SEO tactics into your overall plan.

A well-optimized website helps Google organize and rank your page by making it easier for it to understand the content. In essence, you’re helping Google carry out its tasks more effectively.
All on-page SEO components can be divided into three groups:
- Content elements
- HTML elements
- Site architecture elements
These components are separated into sections below.
Content Elements
The elements of your site’s copy and content are referred to as content elements. This part will mostly concentrate on creating valuable page content that both benefits your users and signals to Google that your website is valuable.
- High-Quality Page Content
The center of on-page SEO is page content. It clarifies to users and search engines what the purpose of your website and business is.
The process of producing high-quality content begins with selecting pertinent keywords and themes. Conduct keyword research by typing phrases into Google to see what websites and competitors’ web pages come up with. Additionally, you can use tools like UberSuggest, AnswerthePublic, and Ahrefs.
Here are some guidelines for producing high-quality page content:
- Naturally, incorporate both short- and long-tail keywords.
- Include interesting and timely visual content.
- Write specifically for your buyer persona (s).
- Solve the issue your audience is facing.
- Make content that others will want to share and link to.
- Use CTAs to offer and product pages to increase conversions.
The page content is the core of the on-page SEO process and gives you the chance to provide value to Google and your site users. Spend enough time and money creating and optimizing the page content since it is the foundation for all other on-page SEO components.
HTML Elements
The elements in your source code are referred to as HTML elements.
Page Titles
One of the most crucial SEO components is the page titles (also known as title tags) of your website.
<title>The Ultimate Guide to Startups</title>
Titles describe what is on the corresponding pages to both visitors and search engines.
To ensure that your web pages rank for the correct reason, be sure to include the focus keyword for each page in the title. Try to use your keyword as casually as possible.
The following are some excellent practices for creating page titles:
- In order to guarantee that your titles display properly, keep them short—under 60 characters, as per Google’s change. Although Google doesn’t set a character limit, its display titles are limited to 600 pixels in length. If you limit the length of your titles to 60 characters or less, they won’t be abbreviated in search results.
- Don’t overuse terms in the title. Modern search engines are sharper than ever and have been built to explicitly monitor (and penalize!) content that is unnaturally filled with keywords. Keyword stuffing makes for a spammy and tacky reading experience.
- Ensure that it pertains to the page.
- Avoid using full capitals.
- Put your company’s name in the title.
- Headers:
Headers, commonly referred to as body tags, are the HTML elements <h1>,<h2>,<h3>, and so on.
<h2>What is a startup?</h2>
These tags let people navigate your content more easily and help search engines understand which parts of your content are the most important and relevant.
Headers should contain important keywords, but avoid using the same ones as the page title.
Your <h1> and <h2> headers should contain your most crucial keywords.
Meta Descriptions:
The brief page summaries that display beneath the title in search results are known as meta descriptions. Although it’s not a search engine’s official ranking criteria, it can affect whether or not a user clicks on your page, therefore it’s equally crucial when performing on-page SEO.
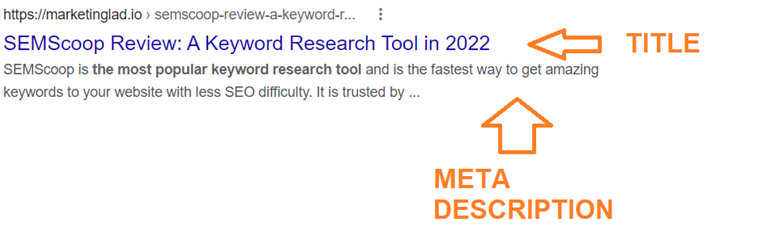
When your content is published on social media (using structured markup, as we discuss below), meta descriptions can be carried over there as well, potentially boosting click-through rates.
What constitutes a strong meta description is as follows:
- Although Google has been known to permit lengthier meta descriptions, keep it to no more than 160 characters.
- Include your keyword or keyword phrase in its entirety.
- Use a full, impactful sentence (or two).
- Avoid using alphanumeric symbols like —, &, or +.
Image Alt-text
Image alt-text for your images functions like SEO. It provides information to Google and other search engines about the subject matter of your images, which is crucial given that Google currently displays almost as many image-based results as text-based ones.
This suggests that visitors may be coming to your website via your photographs. To accomplish this, your photos must have alt-text, though.
When including image alt-text, keep the following in mind:
- Be specific and descriptive.
- Make sure it relates to the general content of the page.
- There shouldn’t be more than 125 characters.
- Don’t keyword stuff and use keywords sparingly.
Structured Markup:
Structured markup, also known as structured data, is the act of “marking up” the source code of your website to help Google identify and comprehend the various components of your content. The highlighted snippets, knowledge panels, and other content elements you see when you conduct a Google search are all made possible by structured markup. Additionally, it explains why your specific page information displays so nice when someone shares your material on social media.
Although structured data is regarded as technical SEO, I’ve included it here because improving it improves the on-page experience for users.
Site Architecture Elements:
The components that make up your website and site pages are referred to as site architecture elements. Google and other search engines can readily crawl your website’s pages and information if it is designed in a certain way.
Page URLs:
Your page URLs should be easy for users and search engines to understand. They are crucial for maintaining the consistency of your site structure as you develop internal pages such as blog entries, subpages, and other kinds of pages.

Here are some ideas for making URLs that are search engine friendly:
- Eliminate the additional, pointless words.
- Use no more than a few keywords.
- If at all possible, utilize HTTPS because Google now considers it to be a good ranking element.
Internal Linking:
Internal linking is the process of using a hyperlink to point to other helpful pages on your website. They are essential for on-page SEO since they point users to other pages on your website, keeping them there for longer, and informing Google that your site is valuable and noteworthy.
Additionally, Google has more time to crawl and index your website pages the longer visitors stay on your site. In the end, this helps Google understand your website better and can make it show up higher in search engine results.
Mobile Responsiveness:
Even for desktop searches, Google started to prefer websites with quicker mobile speeds.

The selection of a website hosting service, site design and theme, and content arrangement that is readable and usable on mobile devices is crucial. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool if you’re unsure if your site is mobile-ready.
Site Speed:
Your site needs to be able to load rapidly whether it is on a desktop or a mobile device. When it comes to on-page SEO, page speed is of the utmost significance.
Google is primarily concerned about the user experience. Google is aware that if your website loads slowly or inconsistently, users are less likely to stay on it. Additionally, site performance may have an impact on conversions and ROI.
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool at any moment to check the speed of your website. Although site speed and mobile responsiveness are both a part of technical SEO. I’m including them here because improving them improves users’ on-page experiences.
Introduction to Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to any SEO tactics that don’t include modifying or adding content to your website.
Off-page SEO and link building were once frequently conflated, however, there are really a number of off-page SEO tactics you may utilize, including:
- Brand building
- Citation building
- Content marketing
- Social media and more.
These tactics help users and search engines understand your website better while also increasing its authority, trust, and relevancy.
Consider it like this:
- Off-page SEO = another website or platform
- On-page SEO = your website
Importance of Off-Page SEO:
Think of off-page SEO as boosting your website’s domain authority. Without it, it might be difficult for your website to outrank sites with greater authority.
Websites with a higher authority typically rank higher than those with a low or no authority because search engines perceive them as being more trustworthy, relevant, and reliable.
Search engines need to know that lots of people use, like, and share your website. One method to show this is through links, however, link building cannot be your first goal. Let’s examine some of the many extra off-page SEO tactics you can use.
Techniques for Off-Page SEO that Work:
Here are some of the off-page strategies you may employ to increase authority and organic search traffic:
- Link Building
- Social Media
- Local SEO
- Content Marketing
Link Building:
Links from other web servers function as endorsements for your domain.
The more votes you receive, the higher you’ll likely rank in search results. In contrast, it will be more difficult to persuade Google that your website is a reliable, authoritative source the fewer votes you receive. Backlinks serve as the vouching for you that you require from other pages. The first off-page tactic on your list should be creating external links.
Links come in a variety of forms that you can acquire:
- Links that you earn from other websites, where customers or editorial publishers mention your brand naturally.
- Built links demand work on your part, such as contacting publishers to get link attribution or mention.
It’s crucial to employ ethical link-building techniques because black hat techniques, such as repeatedly posting links to your website in forums and comment sections, can result in Google penalties.
Check out the complete guide on link building.
Social Media:
More than an SEO strategy, you’ve probably considered social media to be a tool for brand exposure. However, social networking is a fantastic strategy to raise your search engine rating and build your domain authority.
Sharing information on social media and directing users to your website lets Google know that you’re getting traffic from a variety of sources and that your website must contain engaging high-quality content. This is why it’s crucial to regularly interact with your audience on social media and use it to provide content. Increased involvement will probably lead to additional shares, backlinks, and clicks, all of which contribute to the development of domain authority.
Local SEO:
Optimising a website for local search results by using the local SEO method in Google My Business. Firms with physical locations or those that cater to local customers, such as grocers, air conditioning companies, or hair salons stress more to Local SEO.

You have to send signals to local search engines in order for this to function. Why do you do this? Here are a few significant examples:
- Include Google My Business and other regional and national business directories in your company’s listing.
- Respond to reviews left about you on review websites like TripAdvisor and Yelp by claiming your listing.
- Request positive internet evaluations from your clients.
- Maintain a consistent contact list across all digital channels.
Content Marketing:
By providing them with material that meets their requirements and pain areas, content marketing enables you to attract and reach your target audience. You can use techniques like guest blogging, downloadable offers, surveys, and reports in addition to your on-page content marketing initiatives, like blog articles.
These procedures are excellent approaches to increasing website traffic, producing fresh leads, and raising your search engine position.
Consider guest posting, which has several advantages. The first is the potential for expanding your target market’s readership. The second is the worth of the backlink you can obtain by having content as a post/article on a different domain with high authority. Last but not least, guest writing might increase your website’s traffic, a crucial ranking criterion.
Factors for Link Building SEO:
Google and other search engines have become tighter over time about what behaviors they reward and penalize. People started employing a variety of tactics to obtain backlinks after it became clear that link-building was a crucial ranking component. They do anything from post links on forums to buy links.
Once they realized this, search engines began to penalize the use of unethical or unnatural link placements. Here are some things to think about as you design your link-building plan today:
- The quantity of referring domains – According to Google, the more domains that point to your website, the more trust people have in it.
- Link authority – Being cited by high authority domains is preferable to having a large number of referring domains.
- Relevance – The link must be pertinent to your website. Imagine you run a pet toy business. The National Dog Association’s connection is more credible than a lifestyle blogger.
- Anchor text – The precise text that is hyperlinked to your website and serves as its anchor should be informative and pertinent without being spammy.
Conclusion:
The main distinction between on-page and off-page SEO is that on-page optimization aspects are under your control on your own website. The off-site variables are less definite because you have to develop connections with other webmasters to obtain them.
But an effective search engine optimization strategy must concentrate on both tactics if it wants to achieve the greatest ranks in Google, Yahoo, and Bing. There is no clear winner when comparing on-page SEO versus off-page SEO because they both must work together to produce the best results for your website.
P.S. Read our SEO Question Answer Blog here!




