Last Updated on 17/08/2025
Different websites have different URL formats. It is possible for one URL to be formatted for an e-commerce site and another for a blog.
Different URL architectures are frequently used to meet the objectives and requirements of various websites. Ultimately, the URL structure should be SEO-friendly, regardless of the differences between websites.
Both search engine optimization and user experience benefit from properly optimized URLs. URLs rank highly among the factors that search engines use when making decisions.
Similar to page titles, URLs serve as a search engine and a possible visitor’s description of a web page; therefore, they should be precise, alluring, and organized effectively.
We will delve further into the structure of SEO-friendly URLs and how to create them for your website below.
Let’s examine the structure of URLs and discover how they are created, though, before going on to that part.
What is a URL?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a string of letters used on the internet to identify and find a specific resource, such as a web page, picture, video, or file. Each component of a URL is vital for SEO practices (for example, employing HTTPS protocols, acceptable TLDs, relevant subfolders, and so on).
Still, one of the most important components of a URL is the slug. When you create a new page, you must choose a slug. An example is the URL https://marketinglad.io/seo-platforms, where the slug is ‘seo-platforms’.
The Anatomy of a URL
URL consists of many parts:
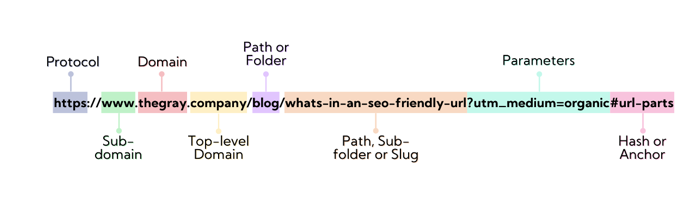
1. Protocol
The very first portion of the URL – the “HTTP” part of “http://www.example.com“. This identifies the protocol used to access the resource, such as HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) or HTTPS (HTTP Secure).

2. Sub Domain
A subdomain in a URL specifies which page of your website the web browser should display. It is the “www.” in “www.example.com.” The use of subdomains helps Google and your visitors understand that your website has more information than just a homepage. They also group your website’s primary content categories.

3. Domain
Your domain name, which (probably) you paid for directly. It tells users that they are on the website of a specific brand.

4. Top-level Domain
The top-level domain (TLD) identifies the sort of entity that your company registers as on the internet.

5. Path
Path refers to anything following the first slash after the domain name (including directories). This is also known as a “relative URL.“

6. Folder/Subfolder
URLs usually have a hierarchical organizational structure. /blog/ is a folder in the sample picture above. If we organized blog material by the year it was published (for example, /blog/2020/what-is-in-a-seo-friendly-url), the /2020/ portion would be a subfolder. It’s a nested version of the parent/child URL structure that’s commonly used for category and subcategory organizing (imagine breadcrumb nesting).

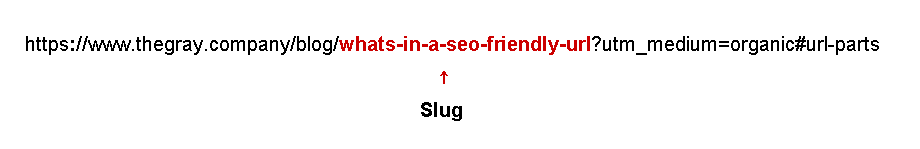
7. Slug
Similar to the path, it only refers to the name of the URL that comes after the last slash, or the particular page you are now reading. The URL slug is the actual filename of the asset in the case of aids (such as pictures, JS, CSS, etc.).
8. Parameters/Query Parameters
Anything following the question mark in a URL, with hashes being the exception. Dynamic URLs, or URL parameters, can alter the content of a website but don’t necessarily do so.

9. Hash/Anchor
Anything following the pound symbol in a URL. Hash-containing unique URLs won’t be accessible to Google; only the portion of the URL that doesn’t contain a hash will be taken into account. They particularly advise against using hashes in URLs as a result.

SEO Tip: Use Replug to create properly optimized URLs connected with your branded domain.
The slug is likely the most significant section for SEO. You must select one of these options each time you create a page or post. An SEO-friendly URL slug will satisfy both search engines and users. URL slugs optimized for SEO, for example, are brief, readily legible and keyword-rich.
But how do you go about developing the best URL slugs for SEO?
So let’s start here!
How to Create an SEO-friendly URL Slug?
When it comes to constructing URL slugs, it’s easy to fall into the trap of simply selecting a few words (representing your page/post) and making them your slug. While a slug that is relevant, accessible, and human-friendly will go you further than a slug that reads like nonsense.
Effective URL slug creation involves MUCH MORE than that.
In fact, there are a few key steps to take in order to develop SEO slugs that increase rankings and visitors.
Let’s go over each of them one by one:
1. Pair your URL Slug with Your Title
- The content of your page should be correctly reflected in a superb URL.
- In this approach, a person will have a clear idea of what to expect when they visit the destination page after seeing your URL.
- They remain because their needs are met on the page.
- Copying your title will help you create an SEO-friendly URL slug.
- Your page’s headline (e.g., title) will produce a reliable URL with a few modifications.
2. Remove Unusual Characters
- Unusual characters should not be used in URLs. They can damage particular browsers and prevent web spiders from seeing your content.
- URLs containing punctuation are difficult to read, making it unpleasant to remember and input the URL into a browser.
All hazardous characters and punctuation (excluding hyphens and underscores) should be removed from your URL.
3. Remove Numbers

URLs with numbers are problematic. They make it more difficult to update your material. To update the slug, I’d have to redirect the old URL to the new URL. Some AI website builders, such as WordPress and Shopify, add a redirect automatically when a slug is updated,
- Furthermore, it’s common to forget to update the URL number while making changes to the other parts, resulting in a mismatch.
- Implementing URL redirection is inefficient. It may result in less link juice being passed through to target URLs.
- Given this, it is preferable to avoid using numbers entirely. When you make modifications to your page/post, you won’t have to adjust the URL slug.
4. Remove Unnecessary Words from Your URL Slug
- Google recommends keeping URLs as simple as possible, and there are likely several reasons for this. For starters, visitors may be put off by very lengthy URLs.
- Second, lengthy URLs are frequently shortened in search results.
Let’s remove any unnecessary information from our possible URL. Stop words (such as “and”, “or”, “but”, “of”, “the”, “a”, etc.) should be avoided in general, as they add unnecessary length to a URL.
5. Reduce Your URL Slug to a Single Keyword
What you’re likely left with at this point is a compressed, keyword-rich version of your title because the majority of titles naturally include keywords. URLs with fewer than 60 characters are more effective. Search engines will not truncate them, and they are easier to read.
But it isn’t all. Short URLs also;
- Make it easier to update the material.
- Keyword importance is increased by using short URLs.
6. Add Keyword Modifiers
Modifiers are words or phrases that provide additional information to your URL. You can potentially rank for long-tail variations of your target keyword by incorporating words like “best,” “guide,” “checklist,” “fast,” and “review” into your content.
For example, in this report for our competitor’s website about SEO experiments, the words “test” and “tester” appear several times.
It could be a good idea to incorporate one of these into our URL. This would help us rank higher for phrases like “SEO tests” and “SEO testing” without significantly affecting our keyword density.
7. Make Your URL Slug Appealing
The organic click-through rate is a crucial ranking factor in search engines. Along with your title tag, your URL has a significant impact on whether or not someone clicks on your listing in SERPs.
Navigating the web often starts with a simple decision: should you search Google or type a URL directly into your browser?
Our URL is concise and centered on our primary target term, making it clear to users in search engines that our page provides exactly what they are looking for, whether they choose to search on Google or type the URL directly.
8. Make a Lower Case URL Slug
- There are certain exceptions to the general rule that web servers regard lowercase and uppercase URLs equally.
- Technically, everything in a URL that comes after the hostname (domain) is case-sensitive, and some dedicated servers handle it accordingly.
- Always use lowercase URLs to be on the safe side and prevent any duplicate content concerns.
9. Replace Spaces with Hyphens
Use hyphens to make the URL more visually appealing. These days, having a clickable URL is essential if you want to drive more organic traffic and achieve higher rankings. Google also recommends using hyphens in URLs.
10. Finish Your URL Slug with a Trailing Slash (optional)
The final step is to finish your URL slug with a trailing slash for visual reasons. A URL that needs a terminating slash or an extension (such as .jpg or .pdf) needs to be completed.
Why is URL Structure Important for SEO?
URLs organize the content on your website. They serve as the interface between your content and the user. A well-formed URL can convey important information about the content of a website, whereas a badly designed URL can be confusing and useless.
Here are some of the reasons why URL structure is essential for SEO:
a. Keywords: The words in a URL can provide search engines with information about the page’s topic. Incorporating relevant keywords into the URL can help the website rank higher in search results for those keywords.
b. User Experience: When it comes to SEO, the most critical component is a great user experience. Utilize a logical URL structure with clear page hierarchies to enhance your user experience. Humans will find it easier to traverse your website if the material is intuitively organized.
c. Navigation: URL structure may also aid people in navigating a website. A logical arrangement of folders and subdirectories in the URL can help people discover similar sites and information more easily.
d. Linking: The use of URLs as anchor text in links is common, and a well-structured URL can give context to the link’s destination. This can help search engines recognize the link’s relevance and improve the page’s ranking.
Conclusion
Are you ready to improve your own URL slugs?
Creating SEO-friendly URLs is a crucial aspect of search engine optimization. Making SEO-friendly URLs that are succinct, descriptive, and easy to read and remember is a best practice. Including keywords in URLs can boost their relevance to search queries.
It is essential to avoid using special characters and unnecessary parameters, as they can confuse URLs and make them more difficult for search engines to crawl.
While it’s not necessary to spend too much time developing SEO-friendly URLs, it does make sense to approach them logically and in accordance with best practices.


